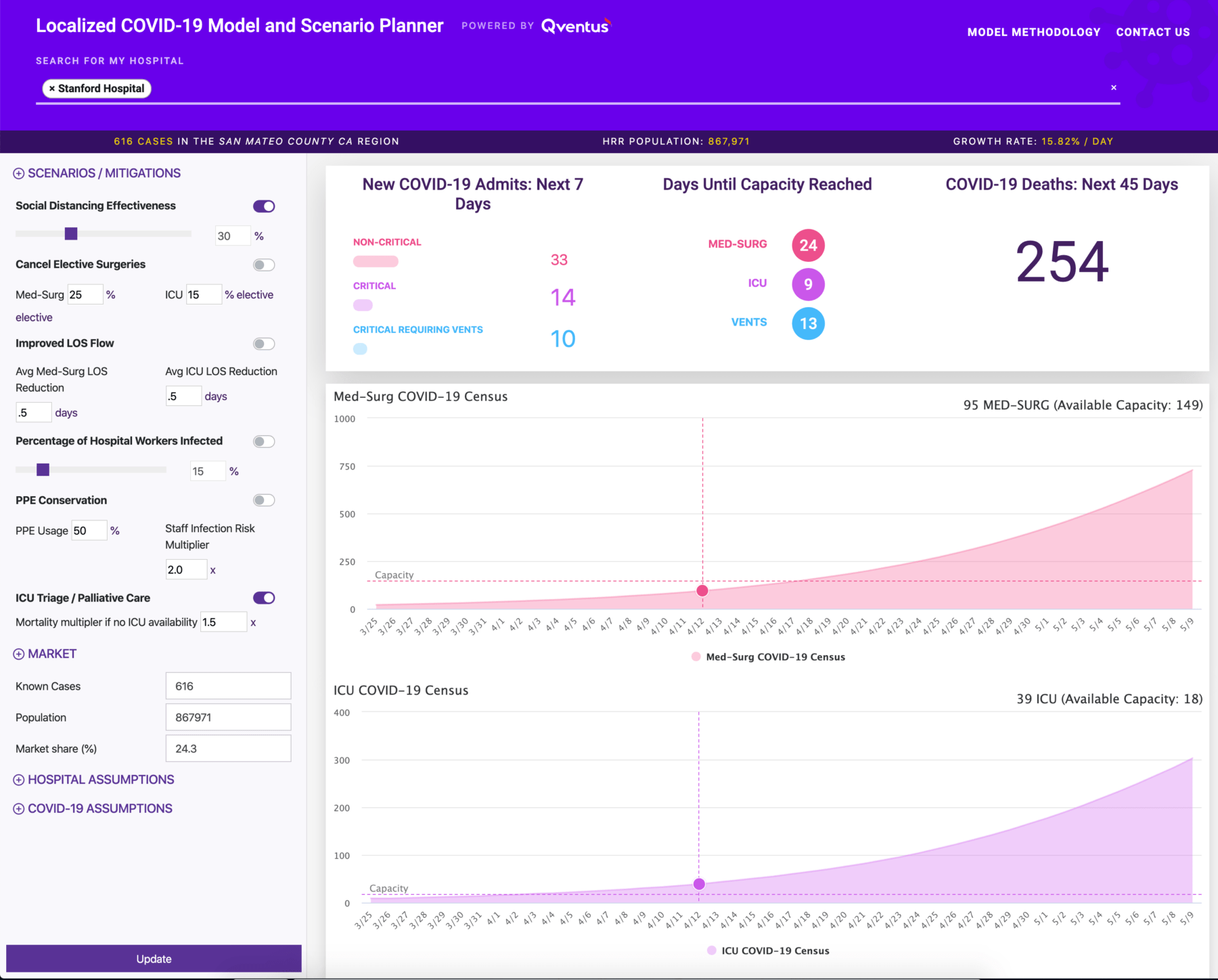
In order to help health systems across the country plan for and mitigate the critical resource constraints expected from a surge in coronavirus patients, Qventus has developed a new COVID-19 planning model designed to support the local decision making needs of hospital operators. This new tool is available to the public now and takes into account the most recent coronavirus research and latest local data on COVID-19 cases.
The new Qventus planning tool is based on a modified SEIR model, and incorporates a live feed of local case count and resource availability estimates. The tool consists of 450 localized epidemiological models that are run and updated daily, providing an up-to-date perspective on the impact of the pandemic in local areas.
In recent weeks, many models and tools have been published that visualize and project the potential impacts of a pandemic-driven surge on scarce health resources. While many of these models are helpful for understanding broad population-level impacts, frontline staff and healthcare leaders have lacked a tool to help them prepare for their specific situations.
This new tool provides broad range of controls and assumptions and provides specific epidemiological planning scenarios, allowing frontline teams to:
- Predict new and cumulative COVID-19 hospitalizations and level of care needs for individual hospitals, multiple hospitals, and regions
- Identify critical capacity constraints for Med-Surg, ICU, ventilator, and PPE resources — e.g., days remaining until you reach capacity — by hospital
- Evaluate the impact of social distancing, PPE conservation, infection of hospital staff, improved length of stay, and other scenarios
- Make decisions based on the most up-to-date data and research related to COVID-19, localized for your health system and market
Methodology Highlight
The key to this model is combining the most current coronavirus research with the most recent COVID-19 case data available on a local basis. Highlights of the model and methodology include:
- Localization: The number of known cases, doubling time (computed from case counts), population demographics, estimated percent of infections reported, expected incubation times, and expected recovery times are used to fit this model to a specific area.
- Market level aggregation: The model uses HRRs (Dartmouth Atlas Project Hospital Referral Regions) instead of counties, zips, or other methods to better align with care-seeking patterns of patients for the geography being modeled.
- Research and Data Driven Assumptions: Wherever possible and appropriate, the model automatically calculates default parameters according to the specific hospital(s) selected. Some parameters are assumed not to vary by region (e.g., incubation period), while others use a single default but remain editable by the user based on any better information they have available (e.g., percent of infections being reported). Access the tool to read the full methodology and assumption sources.
Stay Connected and Contribute
Our goal is to help hospitals and public health leaders plan for and mitigate critical resource shortages, and there are several ways you can stay connected and contribute to this project:
- Register here for access and to receive notifications of ongoing updates as we continue our development of this tool.
- If you are interested in a daily report of forecasted new cases or you would like a guided walk-through of how to use the model for your region, system, or hospital, reach out to us at covid19@qventus.com.
- We have created this solution in cooperation with health system partners, public health departments, and healthcare advisory organizations. Given the speed at which this situation is evolving and the incomplete information at hand, we are eager to update this model as information improves. If you are aware of data or research that can improve these assumptions, please reach out to Anthony Moorman at anthony@qventus.com.